At QLM Group, we understand the importance of selecting suitable food packaging materials for your products. Your packaging is a vital shield, protecting your food, extending its shelf life, and drawing in customers.
Curious about the different food packaging materials out there? Let’s break down the materials, their benefits, and their drawbacks so you can choose the right one.
I. Most Common Types of Food Packaging Materials
1. Plastic
Plastic is versatile and widely used as a food packaging material. These are available in various types, each with its own properties:
- Polyethylene (PE): It’s flexible, transparent, and moisture resistant; it’s ideal for fresh produce, bread, and frozen foods.
- Polypropylene (PP): It is strong, durable, and heat resistant, making it suitable for hot or cold foods and microwavable items.
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): PET is clear and rigid, perfect for bottled beverages and food containers requiring transparency.
- Polystyrene (PS): PS offers good insulation properties and is commonly used for disposable cups and food trays.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): While less common for food packaging due to environmental concerns, PVC can be used for cling wrap and blister packs.
Advantages: Versatile, durable, lightweight, transparent, and cost-effective.
Disadvantages: Environmental impact, limited heat resistance, potential chemical leaching.

2. Glass
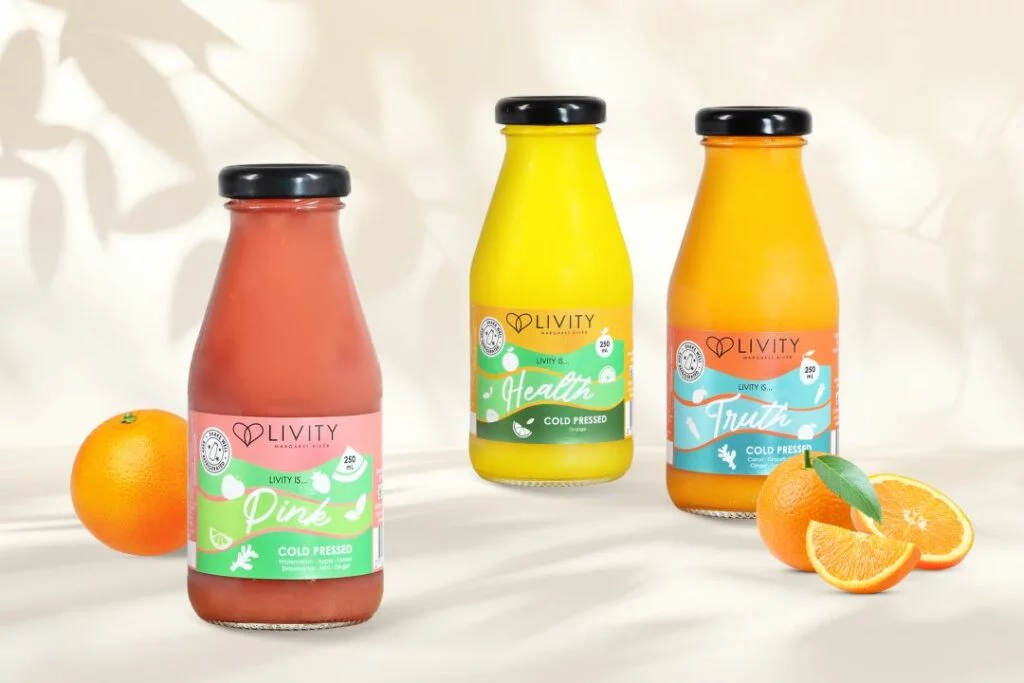
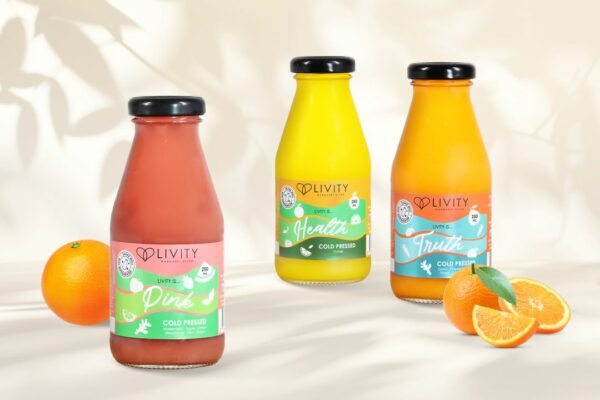
Glass is a non-porous, inert material ideal for food safety and preservation. This type of packaging is commonly used for liquid food products that require labels with a certain level of moisture resistance. At QLM, we take it a step further by using water-resistant labels on our glass packaging for food. This means your product information stays clear and intact, even in damp or moisture-prone environments, ensuring your brand always shines through.
Advantages: Durable, reusable, highly transparent, chemical inertness, microwave-safe, water & moisture resistant.
Disadvantages: Heavy, breakable, limited design flexibility.

3. Metal
Metal containers offer superior protection from light, air, and moisture, ideal for shelf-stable food items. Common types include:
- Aluminium: Lightweight, malleable, and suitable for extended shelf life.
- Tinplate: Steel coated with a thin layer of tin for corrosion resistance.
- Tin-free Steel (TFS): Steel coated with a chromium layer for improved corrosion resistance and recyclability.
Advantages: Excellent barrier properties, durable, stackable, tamper-evident, recyclable.
Disadvantages: High cost, heavier weight, limited transparency.

4. Paper & Paperboard
Paper and paperboard are eco-friendly and cost-effective for dry foods like cereals and bakery goods. So it’s true that those are the common choice in direct contact materials for dry food. But not for wet foods.
To optimise the usability of your food packaging even more, you can even consider adopting barcoding technologies (2D & QR Codes) onto your paper packaging.
Advantages: Sustainable, lightweight, biodegradable, printable.
Disadvantages: Limited barrier properties, not reusable, lower strength.

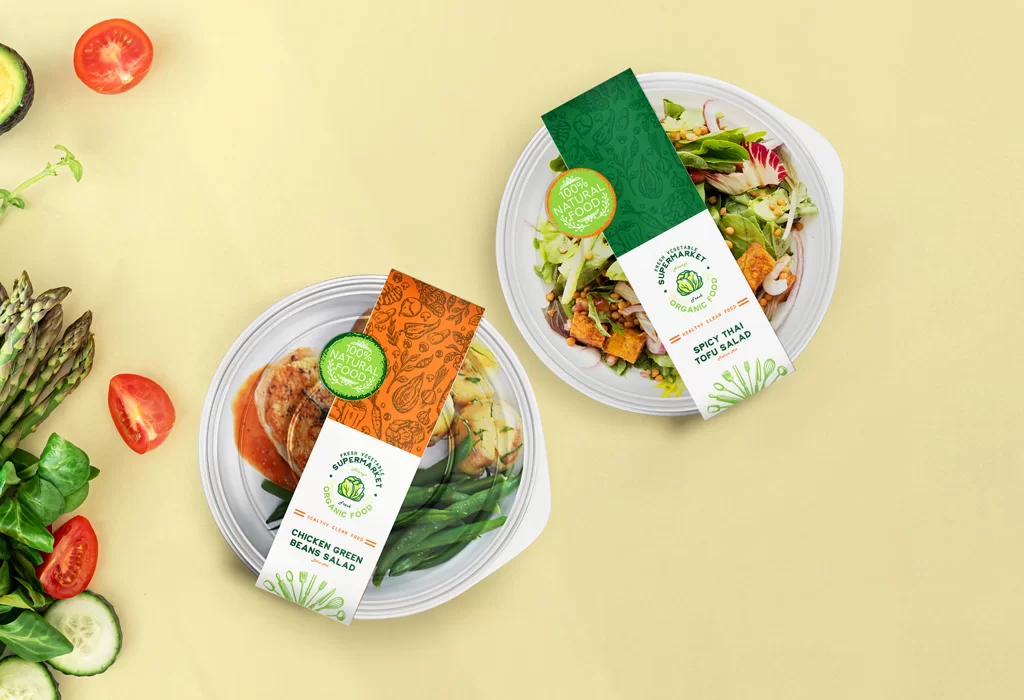
5. Flexible Packaging
Flexible packaging uses plastics, paper, or aluminium laminates to create versatile pouches and bags. For QLM Group, we usually use digital printing technology to deliver precise and vibrant appeal on our flexible packaging for food. This ensures each package effectively showcases your product and stands out on the shelf.
Advantages: Lightweight, flexible, high barrier properties, printing versatility.
Disadvantages: Limited shelf life for some products, potential contamination risks, environmental concerns (recycling and disposal), design limitations, and may not offer the same tamper-evident security as rigid containers.
Explore more: Benefits of flexible packaging

6. Biodegradable & Compostable Materials
As consumers become increasingly eco-conscious, biodegradable and compostable packaging materials are gaining popularity. These materials break down naturally into the environment, reducing the environmental impact of packaging waste. Examples include:
- Plant-based plastics: Made from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane.
- Cellulose: Derived from plant cell walls, offering a strong and biodegradable material.
- Other natural fibres: Materials like hemp, bamboo, and seaweed.
Advantages: Environmentally friendly, compostable, renewable resources.
Disadvantages: Higher cost, limited availability, performance limitations.
II. Choose QLM Group for Your Food Packaging Solutions
At QLM Group, we specialise in providing innovative and sustainable food packaging materials tailored to your needs.
Our team of experts can help you select suitable materials, finishes & embellishments and the right food packaging designs to ensure your products stand out on the shelves.
Our food packaging printing options, finishes, and embellishments include the following:
- Printing: Offset printing, flexographic printing, digital printing, and more.
- Finishes: Glossy, matte, metallic, soft-touch, and textured finishes.
- Embellishments: Foil stamping, embossing, debossing, and holographic effects.
For flexible packaging products, we have the following :
- Stand-up pouches: Versatile and eye-catching packaging for a variety of products.
- Sachets & 3SS Bags: Ideal for small-quantity products and samples.
- Centre seal bags: Flat-bottom bags with a centre seal, perfect for powders and granules.
- Box bottom bags: Sturdy and durable bags with a box-like bottom.
- Side gusset bags: Expandable bags that provide extra space for bulkier products.
Contact us today to discuss your food packaging requirements and explore our wide range of options.